One of the most important and decisive choices you will make in their early life is to vaccinate your children. Parents ought to be mindful of the various vaccines their child should get, what they are doing to avoid illness, and the major gap between mandatory and optional vaccines. The following is a comprehensive guide on the effects of vaccination and gives you the information you need to make better-informed choices on how and when to vaccinate your child. If you have more specific questions about your child, seek guidance from a doctor. Scroll down for the different types of vaccination.
Why Vaccinations Are Important In Childhood
To understand why vaccines are first and foremost necessary, you need to understand the notion of immunity. Immunity is the way the body avoids illness and there are vaccines in order to protect you from certain diseases.
Because the immune system — composed of all kinds of cells, glands, tissues, and fluids — does not accept a foreign germ (known as an antigen), it will send out antibodies called antibodies to combat such invading germs. Then immunity continues to evolve as the antibodies are able to overwhelm and successfully keep the antigen from entering and harming the body. So if the antigen becomes so strong – like in other pathogens that aren’t just normal germs – otherwise the antibodies won’t know enough to interact with the antigen and won’t be able to avoid it from compromising the health.
Globe-wide diseases have been treated and are now generally preventable and rare, due to vaccine campaigns that encouraged vaccine across the globe during childhood. These diseases include pneumonia, measles, rubella, rotavirus, mumps and smallpox among many others.
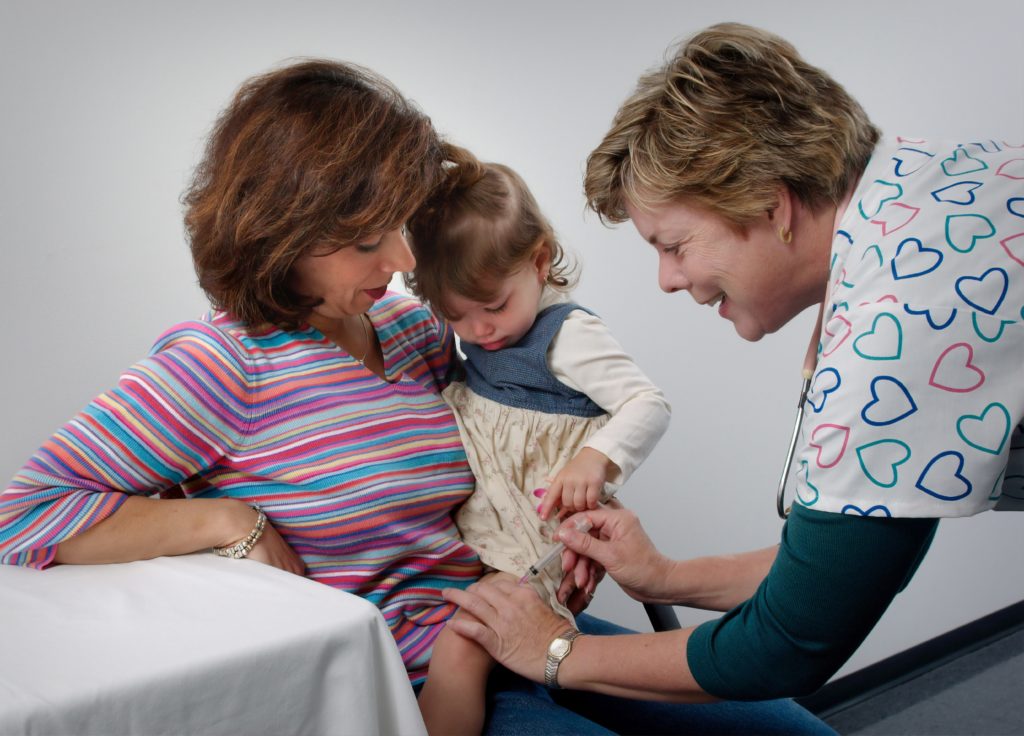
Image Source – Unsplash
When Will Your Child Be Vaccinated?
In general, your children be vaccinated at a very young age, but the exact recommendations can vary from time to time and depend on the vaccine the child is acquiring. Most children receive their first vaccination very soon after they are born and will receive other vaccinations throughout early childhood. You should consult the most recent international and national guidelines in making your decision.
Please contact your doctor to decide how your child should get vaccinated for the best time and date if you have any doubts.
Vaccine Side Effects
Some vaccines can often cause side effects regardless of age. These effects – including fever or soreness – usually are mild and temporary and will fade in a short period of time. You should talk about particular complications and side effects with your doctor, depending on the vaccine, as well as how such effects can be monitored or mitigated (if possible).
In some cases, infants have a severe reaction to their first vaccine. In this case, you can talk to your doctor about the appropriate course of action, as well as the pros and cons of proceeding with the other shorts in the vaccine series.
Which Illnesses Will Your Baby Be Immunized Against?
Some of the most common vaccines for children worldwide are available for diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw), polio, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, gastroenteritis, mumps, measles, rubella, pneumonia, meningitis, Haemophilus influenza type B (Hib), chickenpox, tuberculosis, and pertussis. There are additional vaccines for regional diseases like Japanese encephalitis, which have occurred in some parts of India and other parts of Asia.
1. Hepatitis A
An infectious disease that can have an effect on the functioning of the liver. Normal food, water, and other sick individuals come from contaminated food.
2. Hepatitis B
An invading viral infection of the liver.
3. Rotavirus
A virus infectious that sometimes causes intestine and stomach inflammation (also referred to as gastroenteritis).
4. Mumps
An infectious disease begins with fever, headache and muscle aches, which often leads to tiredness, loss of appetite and swollen glands.
5. Whooping Cough (Pertussis)
A highly infectious respiratory disease that triggers aggressive coughing, which makes it difficult to breathe.
6. Tuberculosis
A disease that is very severe and affects primarily the lungs often spread through coughs and sneezes.
7. Meningitis
Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes.
8. Tetanus
Bacteria from dirt, dust, and manure that penetrates the body through the skin and can cause symptoms ranging from cramping of the jaw and muscle stiffness to rigidity and trouble swallowing.
9. Polio
A debilitating and sometimes deadly infectious disease that invades the brain and spinal cord of a human, and sometimes causes paralysis.
10. Rubella
A contagious viral infection which begins with normal symptoms and causes rash.
Different Types Of Vaccination
In India, the Universal Immunization Program (UIP) is a government scheme that provides for seven specific diseases to be vaccinated and has increased its scope and the vaccines it offers. Under the UIP, and since 1985, the National Immunization Schedule (NIS) has provided parents with a timetable to decide when and how their children will be vaccinated, the so-called “routine immunization.” The Indian Government also collaborates with international bodies such as the World Health Organization (WHO) on the vaccine and viral safety issues.
BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin), DPT (Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus Toxoid), OPV (Oral Polio Vaccine), Hepatitis B, Measles-Lyophilized, TT (Tetanus Toxoid) and Japanese Encephalitis (JE) are currently covered by the infant RI / UIP schedules.
Some of the world’s most popular children’s vaccines are:
1. DTaP
This vaccine provides protection against Diphtheria, Pertussis, and Tetanus.
2. BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin)
This vaccine protects against Tuberculosis.
3. DPT
This vaccine protects against toxoids in diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus.
4. Pneumococcal Conjugate
The vaccine protects against pneumonia and meningitis.
5. Japanese Encephalitis (JE)
This vaccine offers defense against Japanese Encephalitis.
6. Varicella
This vaccine protects against Chicken Pox.
These are some different types of vaccination for childhood diseases.
There are many things that are important to note when it comes to childhood immunization. One of the key concerns is that most vaccines are administered in series and require more than one dose. Although you do not need to restart the sequence if one dose is skipped during that cycle, immunization should be administered as soon as possible, according to schedule. In particular, baby shots and baby vaccines should be administered as soon as possible, but consideration should be given to the child’s well-being and timing of shots.
Vaccination is an effective and easy method of preventing diseases. It can be easily avoided, in turn adding vaccination to prevent disease. In India, there is the RI / UIP scheme in place by India’s government to ensure that these diseases are accounted for and treated at an early age. While you should consider the importance of vaccinations, the various types of vaccines, and your position as parents. Vaccines are generally extremely safe and provide many benefits for your child and other children around them.
Also Read: Vaccines For Child: Typhoid Conjugate Vaccine













