Know About Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome ina child is a condition resulting from exposure to alcohol during the pregnancy of the mother. It causes brain damage and problems with growth. Fetal alcohol syndrome problems vary from child to child, but fetal alcohol syndrome defects are not reversible.
There is no amount of alcohol that during pregnancy is known to be safe to consume. You place your baby at risk of fetal alcohol syndrome if you drink during pregnancy.
Talk to your doctor as soon as possible if you suspect your child has a fetal alcohol syndrome. Early diagnosis can help to reduce problems like learning problems and behavioral problems.
Symptoms Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
The severity of symptoms of fetal alcohol syndrome varies, with some kids experiencing symptoms much higher than others. Fetal alcohol syndrome symptoms and signs can include a mixture of physical defects, intellectual or cognitive disabilities and everyday problems.
1. Physical defects:
It may include:
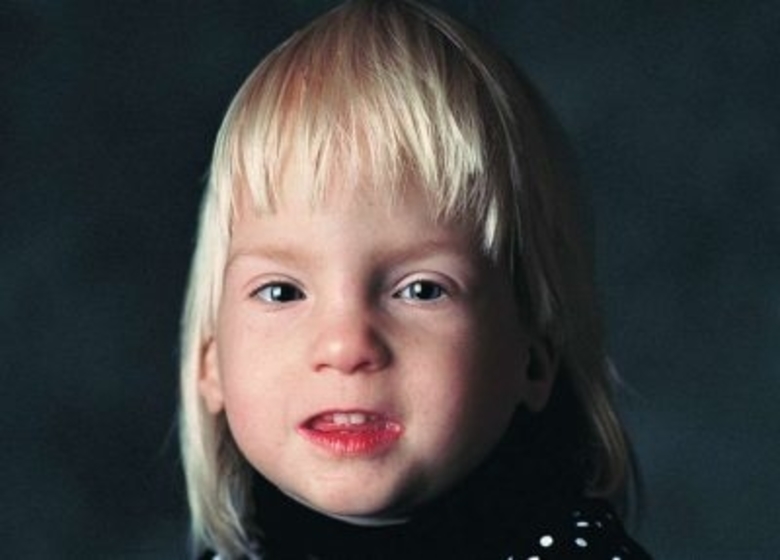
- Different features of the visible face, including small eyes, an extremely thin upper lip, a short upward nose and a smooth skin between the nose and upper lip
- Deformities of joints, limbs, and fingers
- Physical growth slow before and after birth
- Vision or hearing difficulties
- Small circumference of head and size of the brain
- Heart deficiencies and kidney and bone problems
2. Social and behavioral issues:
Problems with how to function, cope with and interact with others may include:
- Trouble in school.
- Difficult to get along with others
- Lack of social skills
- Trouble in adapting change
- Problems with behavior and impulse control
- Problems in planning or working toward a goal
3. Brain and central nervous system problems:
Brain and central nervous system problems may include:
- Lack of coordination or balance
- Intellectual disability, learning disorders and delaying in development
- Poor memory
- Problems with attention and information processing
- Reasoning and problem-solving difficulties
- Difficulty in identifying the impact of choices
- Poor judgmental abilities
- Jitteriness or hyperactivity
- Moods change rapidly
Causes Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
You drink alcohol when you’re pregnant:
- Alcohol enters your bloodstream and passes through the placenta to your developing fetus.
- Alcohol in your developing baby causes higher levels of blood alcohol than in your body because a fetus metabolizes alcohol slower than an adult
- It interferes with your developing baby’s delivery of oxygen and optimal nutrition
- Before birth, exposure to alcohol can harm your baby’s tissues and organs and cause permanent brain damage.
The more you drink during pregnancy, the greater your unborn baby’s risk. Any amount of alcohol, however, endangers your baby. In the early weeks of pregnancy, your baby’s brain, heart, and blood vessels start to develop before you know you’re pregnant.
When To See A Doctor:
Ask your obstetrician, primary care physician or mental health professional for help if you are pregnant and can’t stop drinking.
Since early diagnosis can help to reduce the risk of long-term problems for children with fetal alcohol syndrome, let your child’s doctor know if you’re drinking alcohol while you’re pregnant. Before seeking help, do not wait for problems to arise.
If you have adopted a baby or are providing care, you may not recognize if the biological mother drank alcohol while pregnant — and it may not initially occur to you that your child may have fetal alcohol syndrome. However, if your child has issues with learning and behavior, speak with his or her doctor in order that the underlying cause might be known.
Complications Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
Problem behaviors that may result from fetal alcohol syndrome (secondary disabilities) not present at birth may include:
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Aggression, inappropriate social behavior, and violation of laws and rules
- Misuse of drug or alcohol
- Disorders of mental health like depression, anxiety or eating disorders
- Problems with independent living and with employment
- Inappropriate sexual behaviors
- Early death by accident, homicide or suicide
Prevention Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
Experts know that if women do not drink alcohol during pregnancy, fetal alcohol syndrome is completely preventable. These guidelines can help to prevent the syndrome of fetal alcohol:
-
If you are trying to get pregnant, don’t drink alcohol:
If you haven’t already stopped drinking, stop as soon as you recognize you’re pregnant or if you even assume you would possibly be pregnant. It’s never too late to prevent drinking throughout your pregnancy, however, the earlier you stop, the better it’s for your baby.
-
Continue to avoid alcohol throughout your pregnancy:
In children whose mothers do not drink during pregnancy, fetal alcohol syndrome is completely preventable.
-
Consider abandoning alcohol during your childbearing year:
If you’re sexually active and have sex that’s not protected. Many pregnancies are unplanned, and the earliest weeks of pregnancy may result in damage.
Diagnosis Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
No laboratory test can prove that a child has FAS. It may seem like ADHD to many of its symptoms. Doctors are looking for unusual facial characteristics, lower than average height and/or weight, small head size, attention issues and hyperactivity, and poor coordination to diagnose FAS. They also try to find out whether and if so how much the mother drank while she was pregnant.
It is impossible to cure the symptoms of FAS, but early diagnosis and treatment can improve the development and outlook of a child. Research shows kids are doing better when they:
- Diagnosed before 6 years of age
- During their school years, they are in a loving, caring and stable home
- Are not exposed to violence
- Obtain special education and social services
Treating Of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome:
Therapy can help with problems of behavior and education. Parents can also be trained to help their child. Medication can help to control symptoms such as hyperactivity, lack of focus or anxiety. To see if their treatment needs to be adjusted, a child with fetal alcohol syndrome needs to be closely monitored.
Children and their families with fetal alcohol syndrome can receive support from professionals as well as from other families with this syndrome. Ask the local sources of support for children with fetal alcohol syndrome and their families from your health care provider, social worker or mental health professional.
Also Read: Smoking: Effects On You & Your Baby During Pregnancy